安卓api文档
微软安卓api
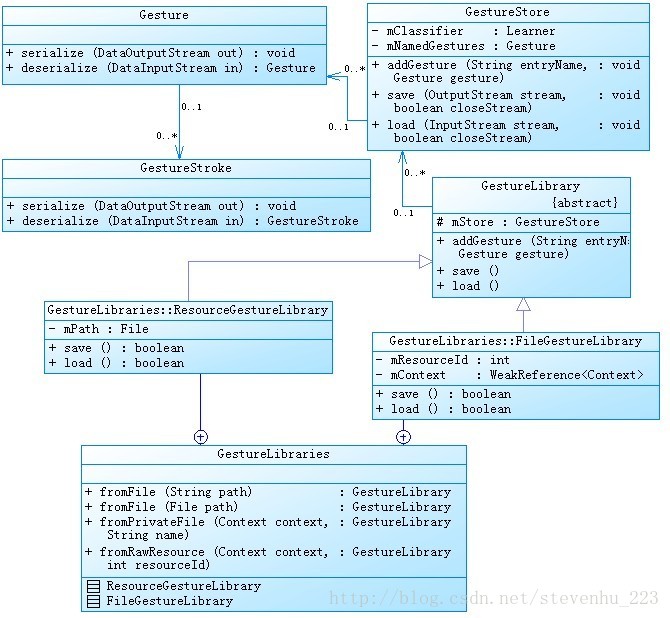
在分析源码之前,我们先来看看有关涉及到手势保存和加载源码类之间的关系,如下图:
通过上图可以知道:
GestureLibrary为抽象类,ResourceGestureLibrary和FileGestureLibrary均继承它;
ResourceGestureLibrary和FileGestureLibrary又作为GestureLibraries的内部类;
GestureLibrary类中的save和load方法为抽象方法,它们的具体实现在子类ResourceGestureLibrary和FileGestureLibrary中;
通过上文Demo的介绍,我们知道,要想保持用户绘制的手势,前提是需要通过创建相应的手势库来实现;如下步骤:sStore = GestureLibraries.fromFile(mStoreFile)–>sStore.addGesture(name, gesture)–>sStore.save()
Step1: GestureLibraries.fromFile(mStoreFile):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public final class GestureLibraries { ... public static GestureLibrary fromFile (File path) { return new FileGestureLibrary (path); } ... }
该方法返回的是FileGestureLibrary对象,FileGestureLibrary为GestureLibraries内部类;
FileGestureLibrary类的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 private static class FileGestureLibrary extends GestureLibrary { private final File mPath; public FileGestureLibrary (File path) { mPath = path; } @Override public boolean isReadOnly () { return !mPath.canWrite(); } public boolean save () { if (!mStore.hasChanged()) return true ; final File file = mPath; final File parentFile = file.getParentFile(); if (!parentFile.exists()) { if (!parentFile.mkdirs()) { return false ; } } boolean result = false ; try { file.createNewFile(); mStore.save(new FileOutputStream (file), true ); result = true ; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Could not save the gesture library in " + mPath, e); } catch (IOException e) { Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Could not save the gesture library in " + mPath, e); } return result; } public boolean load () { boolean result = false ; final File file = mPath; if (file.exists() && file.canRead()) { try { mStore.load(new FileInputStream (file), true ); result = true ; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Could not load the gesture library from " + mPath, e); } catch (IOException e) { Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Could not load the gesture library from " + mPath, e); } } return result; } }
FileGestureLibrary类中的代码实现简介:
1). isReadOnly():该方法实现判断所创建的保存手势文件是否可读;
2). save():实现保存手势的重要方法,在该方法中,实例化所创建文件的输出流,然后根据输出流调用GestureStore的save(OutputStream stream, Boolean closeStream)方法,然后将GestureStore得到的有关手势的信息通过输出流写入文件;
3). Load():该方法实现加载当前已保存手势的文件,当我们需要取出已保存的手势和当前手势进行相似度匹配时,就需要通过手势库加载之前保存的手势文件;
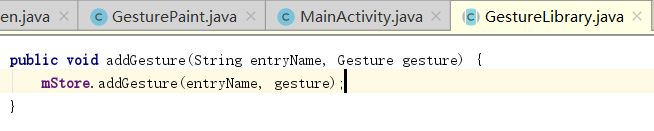
Step2: FileGestureLibrary类没有addGesture方法,所以sStore.addGesture(name, gesture)方法的实现应该在它的父类GestureLibrary中,过程如下:
1 2 3 4 5 private static GestureLibrary sStore;... sStore.addGesture(name, gesture); ...
调用过程:
Mainactivity–>GestureLibrary
GestureLibrary–>GestureStore
GestureStore源码:
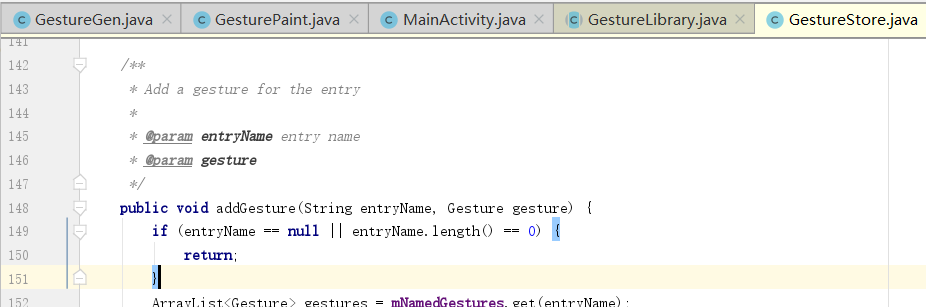
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 package android.gesture;public class GestureStore { ... public void addGesture (String entryName, Gesture gesture) { if (entryName == null || entryName.length() == 0 ) { return ; } ArrayList<Gesture> gestures = mNamedGestures.get(entryName); if (gestures == null ) { gestures = new ArrayList <Gesture>(); mNamedGestures.put(entryName, gestures); } gestures.add(gesture); mClassifier.addInstance( Instance.createInstance(mSequenceType, mOrientationStyle, gesture, entryName)); mChanged = true ; } ... public void load (InputStream stream) throws IOException { load(stream, false ); } public void load (InputStream stream, boolean closeStream) throws IOException { DataInputStream in = null ; try { in = new DataInputStream ((stream instanceof BufferedInputStream) ? stream : new BufferedInputStream (stream, GestureConstants.IO_BUFFER_SIZE)); long start; if (PROFILE_LOADING_SAVING) { start = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); } final short versionNumber = in.readShort(); switch (versionNumber) { case 1 : readFormatV1(in); break ; } if (PROFILE_LOADING_SAVING) { long end = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Loading gestures library = " + (end - start) + " ms" ); } } finally { if (closeStream) GestureUtils.closeStream(in); } } ... }
可以看到手势是存在 一个map里面,键值是自定义的手势名称, 一个手势名称对应着好多个手势(手势数组)
1 2 private final HashMap<String, ArrayList<Gesture>> mNamedGestures = new HashMap <String, ArrayList<Gesture>>();
分析代码添加的核心部分:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public void addGesture (String entryName, Gesture gesture) { if (entryName == null || entryName.length() == 0 ) { return ; } ArrayList<Gesture> gestures = mNamedGestures.get(entryName); if (gestures == null ) { gestures = new ArrayList <Gesture>(); mNamedGestures.put(entryName, gestures); } gestures.add(gesture); mClassifier.addInstance( Instance.createInstance(mSequenceType, mOrientationStyle, gesture, entryName)); mChanged = true ; }
1 private Learner mClassifier;
分析Learner源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 abstract class Learner { private final ArrayList<Instance> mInstances = new ArrayList <Instance>(); void addInstance (Instance instance) { mInstances.add(instance); } ArrayList<Instance> getInstances () { return mInstances; } void removeInstance (long id) { ArrayList<Instance> instances = mInstances; int count = instances.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { Instance instance = instances.get(i); if (id == instance.id) { instances.remove(instance); return ; } } } void removeInstances (String name) { final ArrayList<Instance> toDelete = new ArrayList <Instance>(); final ArrayList<Instance> instances = mInstances; final int count = instances.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { final Instance instance = instances.get(i); if ((instance.label == null && name == null ) || (instance.label != null && instance.label.equals(name))) { toDelete.add(instance); } } instances.removeAll(toDelete); } abstract ArrayList<Prediction> classify (int sequenceType, int orientationType, float [] vector) ; }
Learner.addInstance方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 abstract class Learner { private final ArrayList<Instance> mInstances = new ArrayList <Instance>(); ... void addInstance (Instance instance) { mInstances.add(instance); } ... }
总的来说就是GestureStore.addGesture():
1). 实现将用户绘制的手势存放到mNamedGestures(HashMap类型)中;
2). 通过用户绘制的gesture得到的Instance类型的对象(Instance.createInstance);
3). 将Instance类型的对象存放到mClassifier对象(Learner类型)的成员mInstances集合中;
Step3: 执行完sStore.addGesture(name, gesture)添加手势后,我们接着执行sStore.save()保存所添加的手势相关的信息。sStore.save()方法的实现在FileGestureLibrary中,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public boolean save () { if (!mStore.hasChanged()) return true ; final File file = mPath; final File parentFile = file.getParentFile(); if (!parentFile.exists()) { if (!parentFile.mkdirs()) { return false ; } } boolean result = false ; try { file.createNewFile(); mStore.save(new FileOutputStream (file), true ); result = true ; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Could not save the gesture library in " + mPath, e); } catch (IOException e) { Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Could not save the gesture library in " + mPath, e); } return result; }
1). 通过传进来的File对象创建其对应的输出流(new FileOutputStream(file))
2). 通过创建的输出流执行调用GestureStore的save方法(mStore.save(new FileOutputStream(file), true))
Step4: GestureStore的save方法代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public void save (OutputStream stream, boolean closeStream) throws IOException { DataOutputStream out = null ; try { long start; if (PROFILE_LOADING_SAVING) { start = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); } final HashMap<String, ArrayList<Gesture>> maps = mNamedGestures; out = new DataOutputStream ((stream instanceof BufferedOutputStream) ? stream : new BufferedOutputStream (stream, GestureConstants.IO_BUFFER_SIZE)); out.writeShort(FILE_FORMAT_VERSION); out.writeInt(maps.size()); for (Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<Gesture>> entry : maps.entrySet()) { final String key = entry.getKey(); final ArrayList<Gesture> examples = entry.getValue(); final int count = examples.size(); out.writeUTF(key); out.writeInt(count); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { examples.get(i).serialize(out); } } out.flush(); if (PROFILE_LOADING_SAVING) { long end = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime(); Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Saving gestures library = " + (end - start) + " ms" ); } mChanged = false ; } finally { if (closeStream) GestureUtils.closeStream(out); } }
GestureStore的save方法中代码实现如下:
1). 将执行Step3中得到的mNamedGestures赋值给maps;
2). 通过传进来的输出流创建对应的DataOutputStream类型对象out;
3). 将FILE_FORMAT_VERSION和maps.size()写入out中;
4). 遍历maps,将遍历出的每个ArrayList在maps中的key值和自身存放Gesture的个数count值,分别写入out中;
5). 遍历ArrayList中的Gesture,然后将out作为实参调用执行Gesture的serialize方法;
Step5:继续跟踪到 Gesture的serialize方法,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Gesture implements Parcelable { ... private long mGestureID; private final ArrayList<GestureStroke> mStrokes = new ArrayList <GestureStroke>(); ... public Gesture () { mGestureID = GESTURE_ID_BASE + sGestureCount.incrementAndGet(); } ... void serialize (DataOutputStream out) throws IOException { final ArrayList<GestureStroke> strokes = mStrokes; final int count = strokes.size(); out.writeLong(mGestureID); out.writeInt(count); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { strokes.get(i).serialize(out); } } ... }
Gesture的serialize方法中代码实现如下:
1). 将Gesture对应的mStrokes赋值给strokes;
2). 将Gesture的mGestureID和GestureStroke在strokes中的个数count分别写入DataOutputStream类型的对象out;
3). 遍历strokes中的GestureStroke,然后将out作为实参调用执行GestureStroke的serialize方法;
Step6: 继续跟踪到 GestureStroke的serialize方法,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class GestureStroke { ... public final float [] points; private final long [] timestamps; ... void serialize (DataOutputStream out) throws IOException { final float [] pts = points; final long [] times = timestamps; final int count = points.length; out.writeInt(count / 2 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i += 2 ) { out.writeFloat(pts[i]); out.writeFloat(pts[i + 1 ]); out.writeLong(times[i / 2 ]); } } ... }
GestureStroke的serialize方法中代码实现如下:
1). 将GestureStroke中对应的点数组points和时间戳数组timestamps分别赋值给数组pts和times
2). 将GestureStroke中组成手势的点数count / 2写入DataOutputStream类型的对象out;(pts数组中每两个元素保存一个点对应的x,y值,所以,总点数为数组所有元素个数count除以2)
3). 遍历数组pts,将每个点对应的x,y轴坐标值和时间戳分别写入out;
GestureAPI
巨硬API
Android应用程序编程语言是JAVA,而linux的很多服务程序,包括一些libraries都是用c 或者c++写的,应用程序使用什么样的机制去调用这些系统函数的呢?Java的虚拟机可以通过 System.loadLibrary 来加载本地库,也可以通过JNI函数 RegisterNatives来注册与类相关联的本地方法。在Android中对于一些底层平台相关的native函数大多采用注册关联的方式来调用。
相关链接
Android JNI原理分析